Extended Reality (XR) refers to the combination of Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and related technologies. It provides immersive digital experiences, used in sectors like gaming, education, healthcare, and engineering. Advances in hardware and software have made XR more accessible and affordable, transforming learning and interaction.
What Is The future of XR?
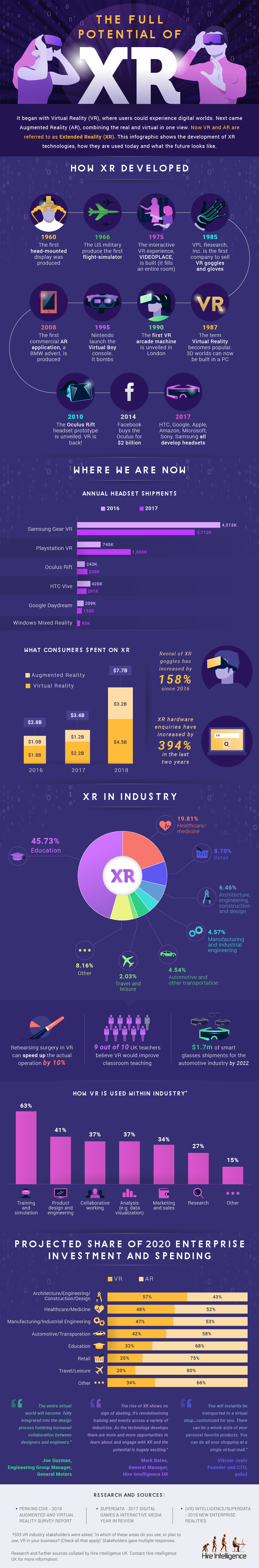
Extended Reality (XR) is the umbrella term now being used to describe Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies. XR has come a long way since the first head-mounted display was built in 1960. Like many significant technological advances, early prototypes were sponsored by the military. In this case, extended reality was used as an immersive technology in training simulators.
More recently, the rise of commercially available and affordable XR hardware can in part be attributed to the entertainment and gaming industry. Consumers spent more than double on XR products in 2018 than they did in 2017 and XR is now a major player in those markets. However, XR’s value as a training and educational tool is now being recognised as businesses wake up to its full potential. This increased awareness can most readily be seen in the growing number of XR-related enquiries we receive, which have increased by 394% since 2016, with a 168% increase in rentals over the same period.
What can Extended Reality be used for?
Additionally, the hardware and software for interacting with XR have improved drastically over the years. XR technologies have improved with sophisticated tech, high-quality imaging and the perception for depth and spatial surroundings. XR software utilises improved programming, such as hand tracking and live movements, so that the environment that XR creates is very similar to the physical environment. Now, a VR headset is available for a fairly affordable price. Products like the Oculus Rift can show students the future, or introduce other emerging technologies.
In terms of industry use, almost 50% of XR is currently used in education. The interactive technology Google Expeditions allow pupils to sit in their classroom and experience virtual worlds. Similarly, apps such as Unimersiv totally immerse students in the sights and sounds of a foreign culture and language, which is proven to aid learning and development. Indeed, 9 out of 10 teachers in the UK recognise that XR technologies would be a benefit in classroom teaching.
In healthcare, there are many application areas of virtual reality, such as being used to train surgeons and doctors. Medical professors at Stanford University have stated their intention to educate their students on anatomy using VR technology, and a research team at Cambridge University is seeking to construct 3D models of tumours that can be explored in incredible detail.
Research into VR uses in this field has found that VR allows specialists to change in situations that are usually changing on the spot. For example, research has shown that rehearsing surgery in VR can speed up operations. It is also being used to allow health & safety trainees, and emergency responders to rehearse disaster scenarios in a safe but very real looking environment. Fergus Drake, CEO of not-for-profit Crown Agents, stated: “Virtual Reality allows us to go some way in accurately conveying the pressures of a humanitarian crisis and we hope it appeals to a new generation of those wanting to work in this life-saving field.”
Aside from educational applications, XR technology is also being used in design, architecture and engineering. Due to the possible application areas of virtual reality, architects can create 1:1 scale models of their projects, which they can then explore, manipulate and test before commencing the build. Similarly, automotive engineers sculpt new cars and engines in Virtual Reality suites, which brings down the cost of building numerous real-world prototypes.
The many possible VR uses are also helping fashion retailers allow consumers to customise their own garments, as well as building virtual shops so customers can browse their goods from the comfort of their own home. Global furniture makers are using AR technology to allow customers to try out new furniture in their own homes before completing their purchase.
These are just a few examples of the current and potential uses of XR technology. Hire Intelligence’s General Manager, Mark Bates, says: “The rise of XR shows no sign of abating, it’s revolutionising training and events across a variety of industries. As VR technology continues to develop there are more and more opportunities to learn about and engage with XR and the potential is hugely exciting”.
It is clear that XR provides users with a creative way to engage in a variety of new environments through simulation technology. With this, XR also offers logical solutions to modern challenges.